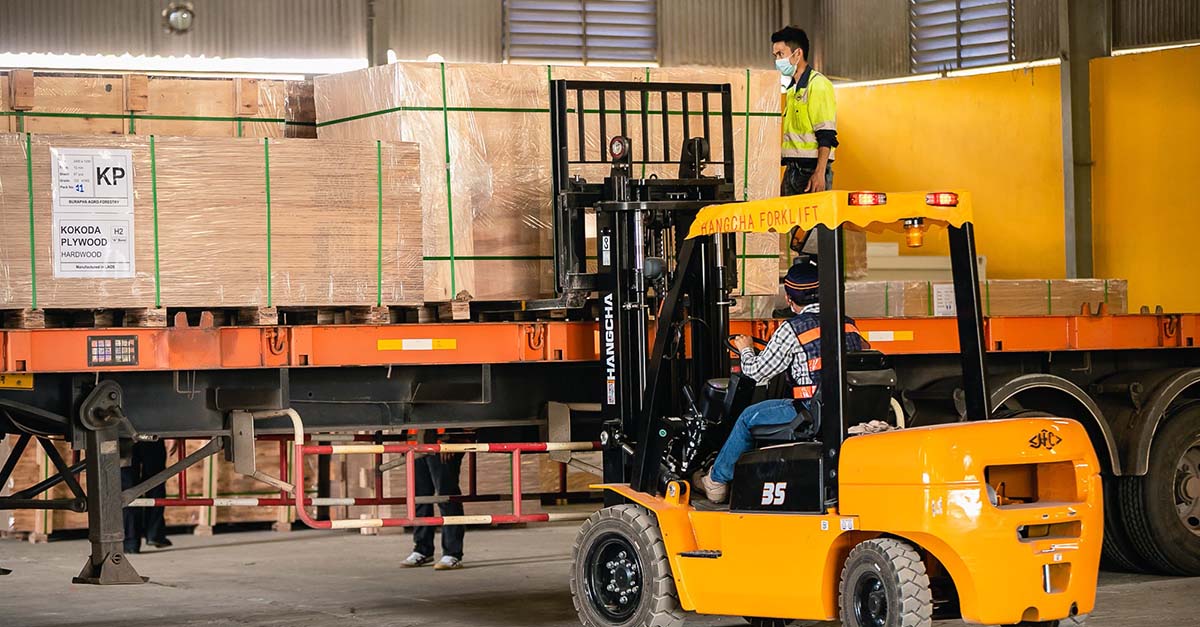
Cambodia's January-August exports to and trade surplus with Canada both rose by around one-quarter on-year, a pattern that is expected to continue, driven by preferential commercial arrangements and initiatives spearheaded by the representative offices of the apex Cambodian trade body, as the Kingdom pushes for a lucrative free trade pact with the world’s ninth largest economy.
In the first eight months of 2022, bilateral trade between Cambodia and Canada came to $804.406 million, up 22.61 per cent year-on-year, with the Kingdom’s exports worth $780.188 million, up 24.03 per cent, and imports totalling $24.217 million, down 10.4 per cent, according to the General Department of Customs and Excise of Cambodia (GDCE).
The Kingdom’s trade surplus with Canada for the period expanded by 25.58 per cent on a yearly basis, from $602.001 million to $755.971 million. As the fifth biggest buyer of Cambodian goods over the first eight months of the year – after the US, Vietnam, China and Japan – Canada accounted for a 4.99 per cent share.
Speaking to The Post on October 3, Cambodia Chamber of Commerce (CCC) vice-president Lim Heng commented that, prior to Covid-19, the Kingdom’s exports to Canada had been on a years-long upward trajectory.
Heng ascribed this year’s export growth momentum on the Canadian market, and its expected continuation for the foreseeable future, to improved diplomatic relations between the two countries, benefits for certain Cambodian goods under Canada’s General Preferential Tariff (GPT) regime, and the existing and subsequent CCC representative offices on Canadian soil.
With Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau reportedly planning to attend the ASEAN Summit in Cambodia next month, Heng anticipates a number of key talks aimed at promoting bilateral trade cooperation between the two countries.
He shared that Cambodian-made goods exported to the Canadian market mainly comprise garments, footwear and travel goods, bicycles, electrical equipment and electronic components, and agricultural products, while imports from Canada include cars, construction materials, and modern technological equipment.
For full article, please read here
Author: Hin Pisei
Source: The Phnom Penh post
The Ministry of Public Works and Transport on Wednesday launched an initiative to improve transport, connectivity, climate resilience, and east-west regional trade across the north of the country.
The Southeast Asia Regional Economic Corridor and Connectivity Project is backed by World Bank financing and is designed to help people in the northern provinces benefit from expanding regional trade and transport connections.
The project was designed to complement the Association of Southeast Asian Nations Master Plan on Connectivity. The new project will upgrade Lao National Road 2 connecting Thailand, Laos, and Vietnam, thus building an east-west corridor that links with existing north-south routes in mainland Southeast Asia.
The upgraded road’s design will protect it from storms, floods, and landslides which are becoming more frequent because of climate change.
Other activities include the development of dry ports, marketplaces, trucking terminals, and locations where farmers can bring their produce for transport to national and foreign markets. A major aim is to improve the ability of local smallholders to market goods that can be traded via the new transport networks.
“We are seeing dramatic improvements in the transport infrastructure running from the north to the central part of the country.”
“However, without local connections to these and other trade routes, most people in the provinces will not be able to take advantage of these new facilities. This is therefore an essential investment in our future,” said Mr. Viengsavath Siphandone, Minister of Public Works and Transport.
Read more: LaoTianTimes
SMALL and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and multinational corporations (MNCs) play an equal role in advancing the sustainability agenda and should work together to do so, said panellists at a discussion held at the SME Centre Conference on Wednesday (Aug 31).
“We all have a responsibility, no matter the size,” said Benjamin Henry Towell, executive director of sustainability at OCBC. “A large corporation uses a whole supply chain of SMEs, and so the relationship between them is quite fluid. Both the SME and MNC need to work together when it (concerns) a whole supply or value chain.”
Similarly, Nigel Lee, general manager of PC vendor Lenovo, said that sustainability was not an individual effort. “In the past, sustainability was about pushing the responsibility to the end-user; now, sustainability is about putting the responsibility on the manufacturer to produce really sustainable products. So we need to connect the dots.”
He noted how Lenovo’s success is dependent on the success of its supply chain partners: “This is a critical part for SMEs, regardless of whether you’re in supply chain or logistics…in the short run, it’s going to impact us one day or the other. So I think the journey has to start with them.”
Benjamin Chua, chief executive of cleaning technology company Speco, said companies should tap the whole ecosystem of partners, including trade chambers and associations. “The opportunities for us to collaborate are out there, especially for SMEs, and we should huddle together as a pack.”
Towell noted that banks can serve as a conduit by connecting solutions providers to customers looking for solutions. “We bank the supply side; we have the demand side as well. So being able to link up those various parts of the ecosystem together to provide their solutions has been very useful, and we’re seeing that in all the different industries.”
Banks can also provide sustainable linked loans to help SMEs transition to becoming greener businesses, Towell added. “There would be targets on greenhouse gas emissions, so in 5 years, you’ll reduce it by, say, 40 per cent year on year and we’ll provide the capital to do that.”
Meanwhile, companies that have been most successful in meeting sustainability goals are those with employees who have fully “internalised” the firm’s sustainability strategy, noted Mayur Singh, co-founder of Green Collective, a collective of sustainable retail brands.
“There are 2 sets of companies: one where employees fully understand what the sustainability roadmap means for the company and its stakeholders, while the other one is where internalisation has not happened in a very good way. It’s more like the KPI is done by the sustainability team.”
He cited the example of outdoor clothing retailer Patagonia, which recruits employees that share the brand’s values of sustainability.
“It’s actually very important to align (at this level), because you have a lot of network effects, which then lead to ideas coming not just from the top to bottom level, but (vice versa). And that is where you can drive a lot of the synergies that value add to sustainability.”
There are many ways for companies to harness this culture of “environmental leadership”, Singh added.
This includes organising talks and workshops, getting employees to form “green teams” - which refers to a group of employees coming together to advance sustainability within the organisation - and even constructing hydroponics walls in the office.
“That belief system that is created within employees can go a very long way in delivering the highest sustainability objectives that the board of your company wants to actually achieve.”
Source: The Business Times
Link: Here
COVID-19 has forced more businesses to think deeper about how to leverage digitalisation and technology, but even today, these tools continue to help companies navigate challenges thrown up by the multiple headwinds the region faces.
Lawrence Loh, head of group business banking at UOB, shared that pre-Covid, between 15-20 per cent of UOB’s SME (small and medium enterprise) customers were thinking about digitalisation.
“Prior to Covid, a lot of SMEs knew about digitalisation, some may even have started transformation efforts. But there wasn’t great impetus to push for more extensive change then,” said Loh.
“Now, 50 to 70 per cent are looking to digitalise… as they get more comfortable with digitalisation and understand the benefits of digital transformation to their businesses.”
According the Asean SME Transformation Study 2022, 66 per cent of the respondents spent more on technology through 2021 compared with previous years.
The same number indicated they are keen to invest more in technology, especially in the areas of digital marketing, customer management, sales, network management and operational processes.
Some 1,500 SMEs in Singapore, Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand and Vietnam were surveyed for this third edition of the study which was conducted in the first quarter of this year by UOB, Accenture and Dun & Bradstreet. The previous editions were published in 2018 and 2020.
Improving operational efficiency
According to Loh, areas that SMEs have indicated interest in relate to tools that streamline payroll, accounting and digital marketing processes.
“These solutions help them manage their operational processes, reduces cost and improves efficiency,” he added.
The UOB SME app, which was launched in August, was developed based on the insights from the study.
For instance, the study found that cash flow remains a key concern for many SMEs (44 per cent), with more than half of businesses (54 per cent) indicating that their existing cash flow can sustain their operations for less than 6 months.
Using the app, SMEs can view their cash flow data, apply for loans, and set personalised foreign currency watchlists.
“One main feature that we see customers using the app for is cash flow analysis, which can be viewed on the interactive dashboard. They are also able to track their accounts receivable and accounts payable. The digitalisation helps them to view their cash flow real time and manage their business more efficiently on the go,” he said.
Brando Tan, director of Band World (Asia), who tested the app during its soft launch, said he appreciated that the app offered him real-time view of his business transactions. He used the app to set up a personalised foreign currency watchlist and was able to receive alerts when his limits were reached.
The app also allows SMEs to manage their human resources, payroll, logistics and digital marketing needs. Additionally, the UOB SME app allows business owners the flexibility to transact on the go. Other products in the market are generally contained to desktops only.
The bank is aiming to have about 200,000 SME users onboard the app. It is currently available to customers in Singapore, Malaysia and Vietnam, and will be progressively launched in Indonesia and Thailand by the end of next year.
Looking ahead, Loh said one of the features they are currently implementing is enabling access to general insurance solutions, offered digitally through the app. Further down the road, other features that could potentially be implemented include cashflow comparisons for specific industry peer groups. This will be in addition to looking at how they can further simplify transactions via the app.
Meanwhile, even as the pandemic draws on and regional governments introduce reopening measures, business optimism is steadily returning to pre-pandemic levels, with 1 in 2 SMEs expecting an increase in revenue from 2022, according to the report.
That being said, they continue to look to the government for financing. Perhaps unsurprisingly, 74 per cent of the survey respondents highlighted government funding schemes as their preferred source of funding, up from 34 per cent in the 2020 survey.
This is likely attributed in part to the increased availability of support schemes during the pandemic, which has built a level of awareness among SMEs.
Specifically, respondents considered active support in the creation of digital infrastructures for SME banking (77 per cent) and funding for the adoption of digital technologies (77 per cent) as the most useful forms of government support initiatives.
But it is not just funding SMEs were keen on. They also indicated that they looked forward to receiving more diverse forms of support from their governments. Indeed, respondents from all markets agreed that offering a wider variety of non-financial government schemes, such as mentorship and peer support networks (56 per cent), is the preferred way for the government to be a better partner to businesses.
“SMEs expressed a strong need for tripartite collaboration between banks and the government. Essentially what they want is to have a strong network to tap on. From UOB’s perspective, we are now able to give provide SMEs with wider reach to a larger customer base, hence enabling growth,” said Loh.
They are also working with businesses to forge meaningful collaborations. For instance, through UOB’s BizSmart partnership with Exabytes, the bank is able to help its customers who do not have any digital experience build customised e-commerce websites in just 15 minutes, therefore helping them build increased online presence and distribution channels
On the supply chains front meanwhile, the study found that businesses are increasingly focusing their investments on digital tools that can make their supply chains more flexible.
“As business volatility continues for a protracted period, SMEs must build greater resilience in their supply chains. SMEs should keep themselves informed on supply chain enhancements and change trends during the pandemic, and develop new capabilities with the longer term in mind,” noted the study.
Logistics companies such as GKE Corporation, Pacific Logistics Group and Legend Logistics are examples of local companies that have successfully crowdsourced inovative solutions in data analysis and automation, thereby enabling them to enhance their end-to-end supply chain visibility and operations.
Lee Pak Sing, assistant chief executive officer, trade, connectivity and business services at Enterprise Singapore, also highlighted that companies have realised the importance of tapping on digital solutions, such as data analytics.
This, he told The Business Times, allows them to detect and implement informed countermeasures quickly in response to unexpected events such as port congestion and tightened border controls.
Source: The Business Times
Link: Here
JUST months after Vietnam reopened to international visitors, some Singapore companies are wasting no time heading to the South-east Asian country in search of opportunities, in areas from tech to lifestyle.
Emile Dumont, founder and chief executive of sports massage studio The Posture Lab, said that Vietnam has a growing fitness and wellness trend, but a lack of proper accreditation for trainers. This gap is what The Posture Lab, which also runs an academy, hopes to fill.
"That's why we actually want to come in with that first-mover advantage to build up that whole ecosystem aspect, before we actually build or develop even just gym management or setting up gyms," he explained.
The plan is to work with universities to offer internationally-accredited fitness and wellness courses. This also creates a pipeline of manpower for when the business is ready to scale, Dumont told The Business Times (BT).
To get a head start on these plans, the company participated in the Global Innovation Alliance (GIA) accelerator programme in Vietnam in August.
Formed by a partnership between Enterprise Singapore (EnterpriseSG) and venture capital firm Quest Ventures, the programme is curated for "high-potential" startups and companies, with masterclasses, market immersion programmes and ongoing mentorship.
Earlier batches did not get to visit Vietnam as borders were closed due to the Covid-19 pandemic. But now that borders have reopened, Quest Ventures said that new applications for this fifth edition were up 14 per cent compared to the previous run, despite a shorter application window.
Only 5 companies were ultimately chosen for the programme, which took them to Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City over 5 days jam-packed with networking events and meals with potential partners and investors, as well as meetings with mentors.
Describing the experience as "amazing", Dr Tan Yeow Kee, founder and CEO of fall detection startup SoundEye, said he found 2 partners during the trip. One of them is Canon Vietnam, with which Dr Tan had already been in contact prior to the trip.
"Before I came, I already started to look for partners, otherwise it's going to be a bit tough. So I think a few steps ahead," he said. He plans to return to Hanoi this month to meet a customer.
Since 2020, 45 Singapore-based startups, including the latest cohort, have participated in the Vietnam GIA programme.
Kow Juan Tiang, executive director for South-east Asia at EnterpriseSG, said 3 startups have since set up a presence in Vietnam, while more than 10 are in discussions with potential partners on possible project collaborations.
Beyond the GIA, companies can tap schemes such as the Market Readiness Assistance grant, which provides support for overseas set-up, business matching and market promotion. Businesses can also apply for the Enterprise Development Grant to increase their in-market competitiveness.
EnterpriseSG also has 36 global overseas centres to help companies navigate foreign markets. In Vietnam, these are in Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City.
Nguyen Phi Van, chair of Vietnamese government-backed Saigon Innovation Hub, credits the good inter-government partnership for many Singapore companies' interest in Vietnam.
"Singapore has always been one of the strongest partners of Vietnam pre- and post-pandemic. After the pandemic, the first 10 delegations I receive in Vietnam are all Singaporeans," she said with amusement.
Singapore companies' appetite for the Vietnam market can also be seen in the flows of capital into the country.
Singapore was Vietnam's top foreign investor for the second straight year in 2021, and still holds the pole position for the first half of 2022 with direct investment contributions totalling S$4.1 billion, according to Vietnam's Ministry of Planning and Investment.
The Singapore Business Federation (SBF), which set up a Singapore Enterprise Centre (SEC) in Ho Chi Minh City in January last year, said companies are ready to head here now that the pandemic is fading away.
For the past 2 years, the SBF could only hear companies expressing interest; now, with more information and greater confidence, it can "see a lot of companies flying in", said Amy Wee, country head at the SEC@Ho Chi Minh City.
Wee, who shuttles between Ho Chi Minh City and Singapore every few weeks, manages the GlobalConnect@SBF in the southern Vietnamese city. From Aug 22 to 26, an overseas market workshop was held there for 16 companies which are new to the market and would like to meet potential customers and vendors.
One of the companies is Singapore fashion store iORA, which hopes to make Vietnam its second overseas market after having expanded into Malaysia in 2007.
Speaking to Singapore reporters on the sidelines of the workshop, iORA's marketing director Teo Toon Lin said it was very important to do sufficient groundwork before deciding to expand overseas.
"We want to really have an opportunity just to check things out a bit and get ourselves familiar. Looking for suitable partners might take some time too, because you want to work with people who share the same ideas," she noted. "And you want to make sure that you trust your partner to do certain things here correctly when you're not around."
Ripe economic conditions
Following sluggish growth last year, Vietnam has made a swift recovery from the pandemic, with gross domestic product (GDP) expected to grow 7.5 per cent year on year in 2022, according to estimates by the World Bank. With a population of close to 100 million, Vietnam's middle class is also believed to be among the fastest growing in Asia.
While these alone are attractive factors for potential investors, market watchers note several other enablers that make Vietnam stand out: social and political stability, relatively low operating costs, easy access to labour, as well as a bevy of business and investment incentives offered by the pro-business government.
The government has been "very welcoming to invite foreign businesses to actually develop themselves in Vietnam" and has encouraged young Vietnamese to upskill, SBF's Wee added.
EnterpriseSG's Kow has observed that many Singapore companies, particularly in tech, choose to set up in Vietnam as it has a ready pool of tech talent, reducing the time needed to set up shop. "These talents can also help Singapore companies gain market insights and navigate local business practices, as well as bridge language barriers as they look to collaborate with in-market players," he said.
The country's strategic location -- bordering China, Cambodia, Laos and Thailand -- and long coastline make exports easy, SBF's Wee pointed out.
Vietnam's recent history also presents certain unique conditions, said Taku Tanaka, co-founder and CEO of Ho Chi Minh City-based food-sourcing startup Kamereo that last year raised US$4.6 million in a Series A funding round.
"Compared to other countries, Vietnam doesn't have very big conglomerates yet. Because of the Vietnam War, most of the big corporates started from the 1970s or 80s," pointed out Tanaka, adding that most conglomerates are still managed by their first-generation founders and chief executives.
Noting that 98 per cent of businesses in the country are small and medium enterprises, he said: "So the conglomerates are not really strong enough, and I think there's still a little room for even foreigners to come in to do something better than what there is right now."
Source: The Business Times
Link: Here
Laos reported a trade deficit of USD 166 million in August as it imported substantially more goods than it exported from the country. There has been an increase in the trade deficit by USD 52 since July.
According to the latest information from the Lao Trade Portal website, the overall value of Laos trade was USD 1.02 billion in August this year, with USD 427 million in exports and 593 million dollars in imports.
The major export sources included iron ore, copper ore, paper, paper-made products, gold ore, wood pulp, and waste, asphalt, fertilizer, paper, sugar, beverages, clothing, and shoes.
Meanwhile, major imports comprised Diesel and mechanical equipment, land vehicles, wood pulp, and waste paper, beverages, plastic products, living animals, minerals, steel and steel products, and magnetic steel.
Laos’ biggest export destinations were China, Vietnam, Thailand, Australia, and Hong Kong while the top nations it imported from were Thailand, China, Vietnam, The United States, and Switzerland.
Soruce: LaoTainTime
Government-owned Ghanim International Corporation is set to begin operating Brunei’s biggest integrated food and beverage (F&B) manufacturing facility by the year’s end, which is expected to significantly bolster local production for domestic and international demand.
Located at the Salambigar Industrial Park, the multi-million dollar Brunei Food Industry Development Multipurpose Manufacturing and Processing Facility (BFID) is a joint project between Ghanim and Darussalam Enterprise (DARe).
In addition to serving as Ghanim’s manufacturing base for their bruneihalalfoods product range, BFID will also be open to local businesses to develop and manufacture their own products.
With substantial production capability, BFID is expected to lower manufacturing costs, while also increasing product marketability by acquiring international standard certifications for its facilities.
Source: Biz Brunei
Read the full article here
Source: ZAWYA